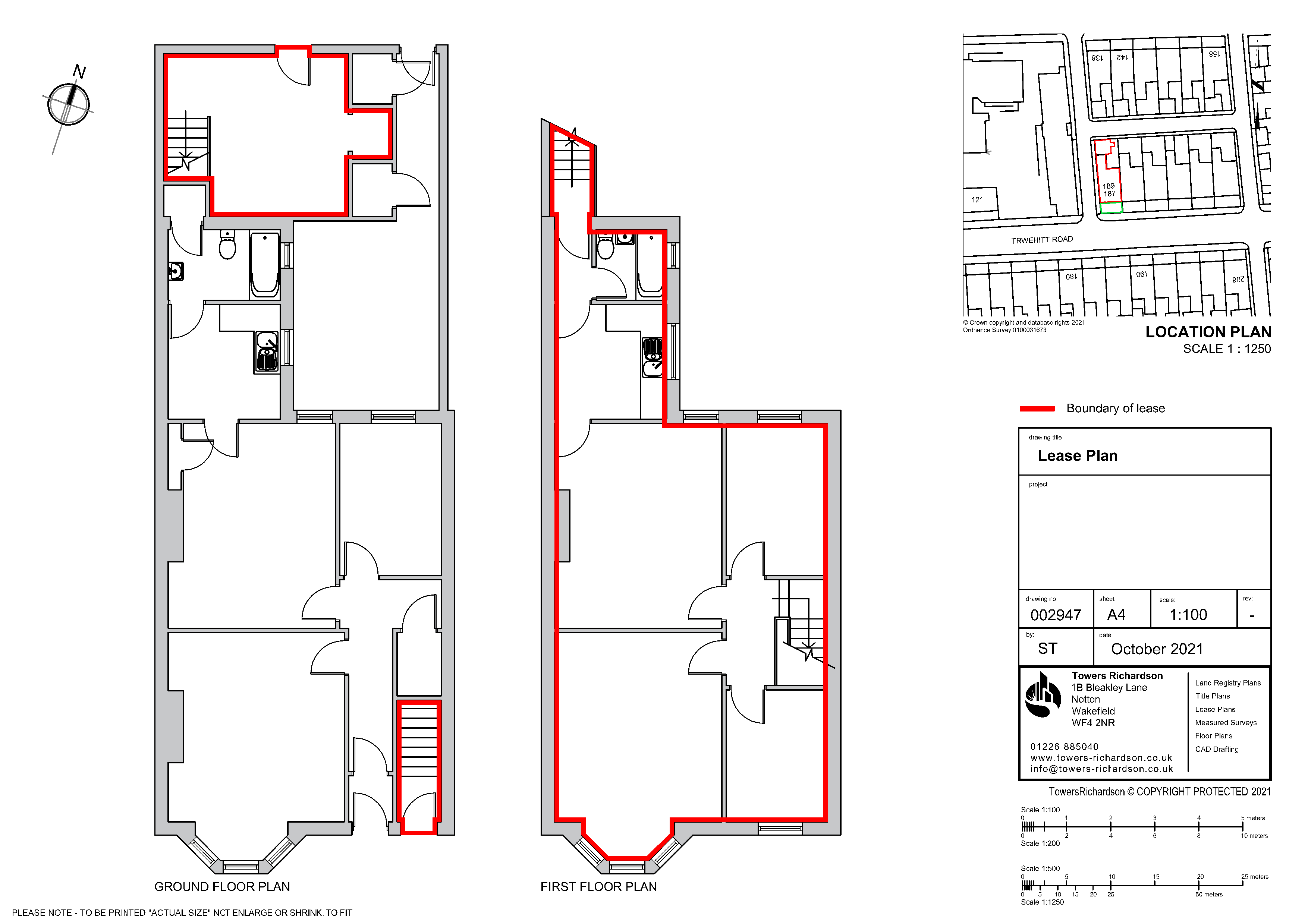
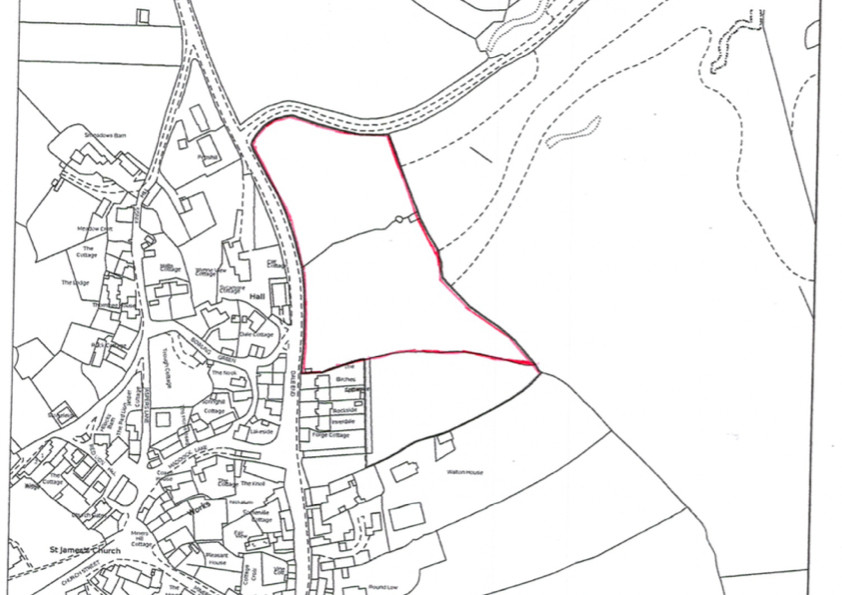
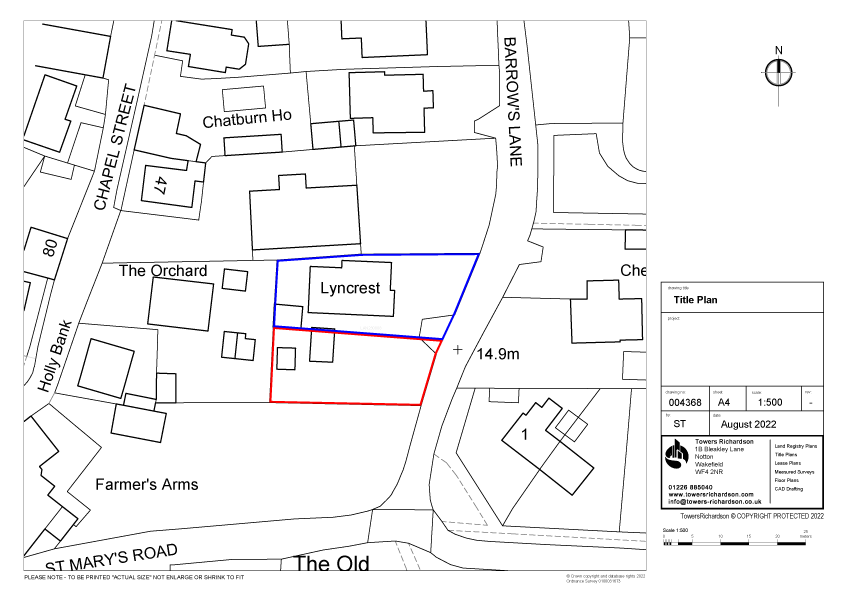
When a property is registered, a unique reference known as a title number is assigned, and both a register and, in most instances, a title plan are prepared.
The register contains crucial details about the property, including the names of the legal owners and information regarding any mortgages, rights of way, or other legal considerations that may impact it.
Additionally, the register provides a description of the property, typically its postal address, and specifies whether it is held for a specific duration under a lease (leasehold) or if it is owned outright (freehold).
While it is generally recommended to review the register and plan together, for the purpose of our discussion here, we will specifically focus on the register.
Key Components of a Register:
- Property Details: The register includes precise details about the property, such as its address, boundaries, and any unique identifiers like title numbers.
- Ownership Information: It outlines the current owner of the property and details of how they acquired it. This section may also include restrictions or limitations on the property, such as easements or covenants.
- Price Paid/Value: In some cases, the title register may include information about the price paid for the property during the last transaction. This can be useful for assessing the property’s market value.
- Mortgages and Charges: If there are any mortgages or charges on the property, the title register will provide details about them. This information is crucial for potential buyers or lenders, as it indicates existing financial commitments related to the property.
- Easements and Rights of Way: The register outlines any easements or rights of way that affect the property. This could include access rights or permissions for utilities to pass through the land.
- Restrictions: Restrictions on the use or development of the property may be specified in the title register. These restrictions are legally binding and must be taken into account by current and future owners.
- Leasehold Information: For leasehold properties, the title register includes details about the lease, including its duration, conditions, and any ground rent payable.
Importance of the Register:
- Legal Clarity: The register provides a clear and official record of property ownership, reducing the risk of disputes and legal uncertainties.
- Transaction Transparency: When buying or selling a property, the title register is a crucial document for both parties. It ensures that all relevant information about the property is disclosed and understood.
- Mortgage Lending: Lenders use the title register to assess the risk associated with providing a mortgage for a particular property. It helps them understand any existing charges or restrictions.
- Due Diligence: Potential buyers and investors use the title register for due diligence purposes, investigating the property’s history and legal status before making a purchase.
In summary, a title register is a foundational document in the real estate landscape, providing transparency, legal clarity, and essential information for various stakeholders involved in property transactions.
You can read more on the HM Land Registry website here.